Designing for Accessibility: Key Principles and Techniques to Enhance User Experience
Introduction
In an increasingly digital world, designing for accessibility has become essential to ensure that everyone, regardless of ability, can fully engage with technology. This article will explore key principles and techniques for creating accessible designs that cater to a diverse user base, enhancing overall user experience and promoting inclusivity.
Understanding Accessibility and Its Importance
Accessibility in design refers to creating products and experiences that are usable by people with a wide range of abilities, including those with disabilities. Inclusive design not only benefits users with disabilities but also improves the user experience for everyone by making products more user-friendly and adaptable.
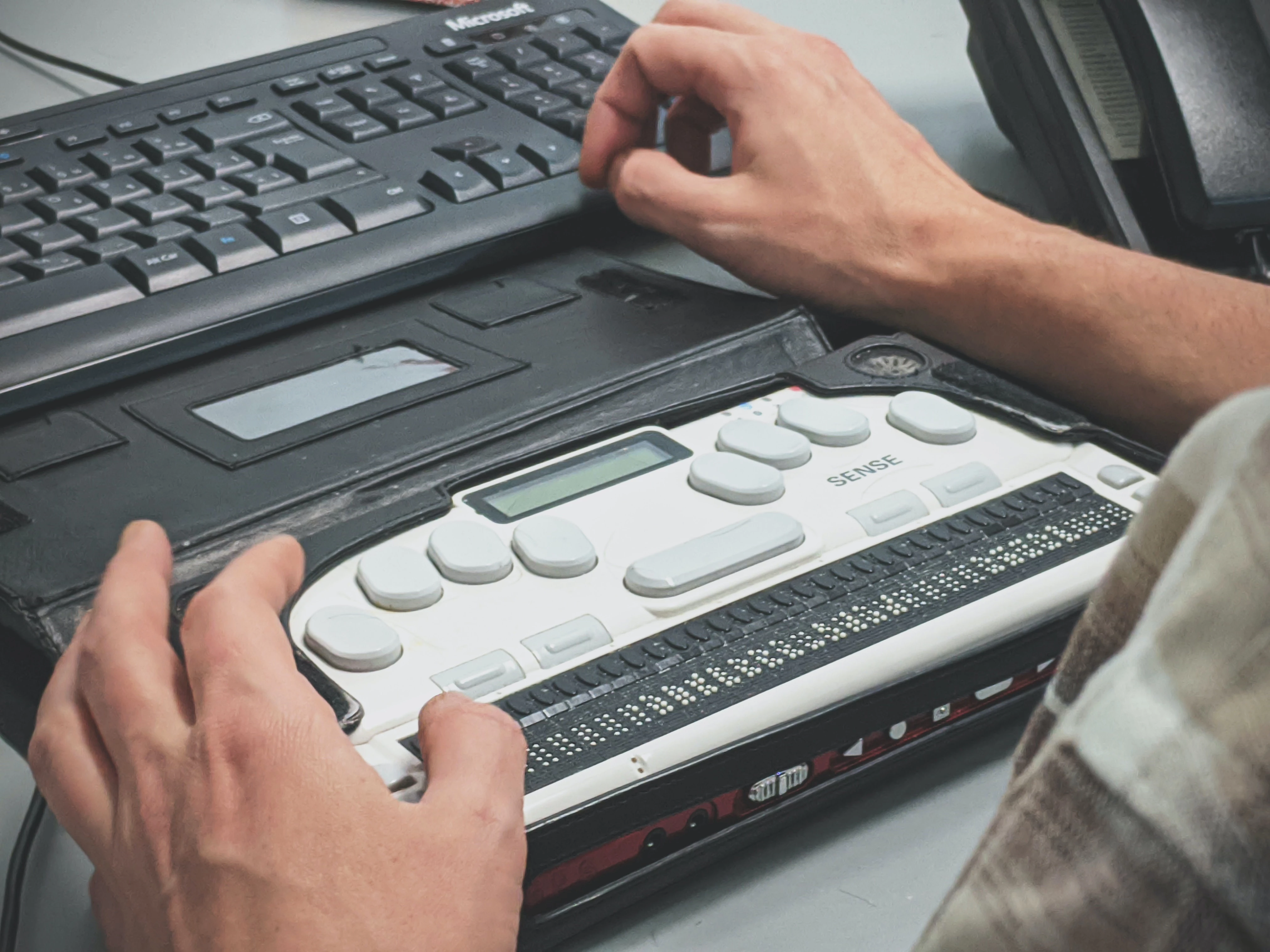

Key Principles of Accessible Design
To create accessible designs, it's important to adhere to these key principles:
- Perceivable: Ensure that information and user interface components are presented in a way that users can perceive, regardless of their sensory abilities.
- Operable: Make user interface components and navigation operable for users with various physical or cognitive abilities.
- Understandable: Create designs that are clear, concise, and easy to understand for users with diverse cognitive abilities and language proficiencies.
- Robust: Ensure compatibility with a wide range of assistive technologies and future updates.
Techniques for Designing Accessible User Experiences
- Use of proper color contrast: Make sure that text and other important elements are easily distinguishable from the background to assist users with visual impairments.
- Clear, legible typography: Choose fonts that are easy to read and have appropriate font sizes, line spacing, and letter spacing.
- Keyboard accessibility: Ensure that all interactive elements are accessible using keyboard input alone, making your design usable for users with mobility impairments.
- Descriptive labels and alternative text: Provide descriptive labels for form fields and alternative text for images, making your content accessible to screen readers for users with visual impairments.
- Consistent, logical layout and navigation: Maintain a consistent layout and navigation structure across your website or app, making it easier for users with cognitive disabilities to understand and use your product.
- Designing for multiple devices and screen sizes: Implement responsive design techniques to ensure that your design functions well on various devices and screen sizes, including those used by people with low vision.
Testing and Iterating for Accessibility
Conclusion
Designing for accessibility is a crucial aspect of modern UX design. By following to key principles and implementing proven techniques, we, designers can create inclusive, user-friendly experiences that cater to a diverse user base. By continuously testing and iterating on your designs, you can ensure that your products are accessible and enjoyable for everyone, regardless of ability.